CARIRI’s Effluent Management Solutions Department (EMS) is equipped with up-to-date, green and clean technology and competent staff with years of experience to better serve the needs of the industrial, commercial and agricultural sectors. CARIRI’s EMS staff is passionate and committed and is always ready to embark on a holistic approach to wastewater management through the use of tools including treatability studies, customised interventions and administrative interventions to focus on achieving clean water, better effluent management and beneficial reuse of wastewater as a resource.
Sustainable Management of water resources and access to safe water and sanitation are indeed essential for unlocking economic growth and productivity in Trinidad and Tobago.
The United Nations sustainable development Goal 6, Local legislation(Water Pollution Rules ,2019) and policies including National Environmental Policy (NEP) seek to ensure safe drinking water, treated discharge and effluent charter a path for management of water and wastewater. It acknowledges the importance of obtaining safe levels of wastewater to comply with healthy ecosystems and fall within permissible levels of the three schedules of the Water Pollution Rules.
Our Services
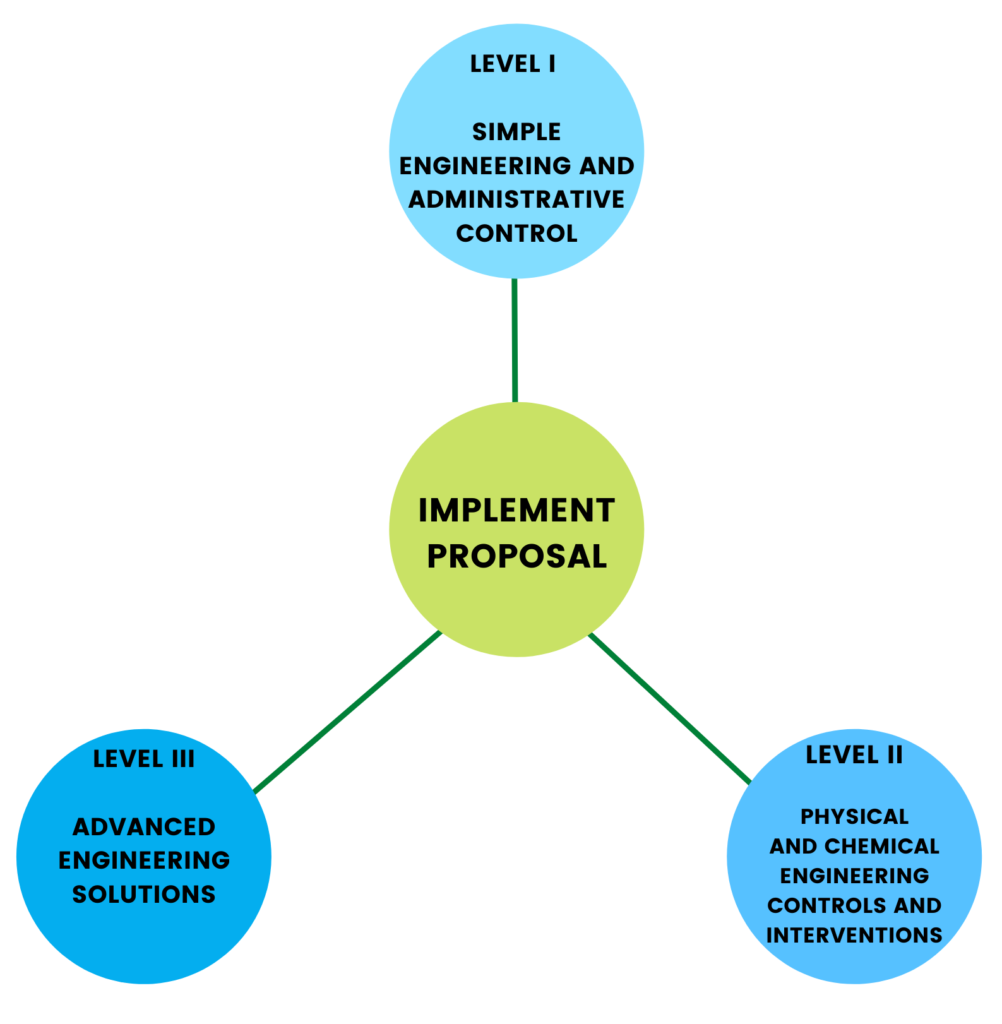
Level I: Simple Engineering and Administrative Controls
- Pollution and Prevention Control Plan (PPCP)
- Best Management Practices Plan (BMPP)
- Quality Assurance Project Plan (QAPP)
- Management of Certificates of Environmental Clearance (CECs)
- Technical Consultancy – Treatability Study
- Training and Workshops on Water and Wastewater- Client Specific and Customized
- Certification Training on Water Sampling Techniques (EMA requirements)
Level II: Simple Engineering and Administrative Controls
- Retrofitting of Sumps and Preparation of Design Specifications
- Basket screen
- Sample collection for efficiency
- Oily Water Separators and Grease Traps
Level III: Simple Engineering and Administrative Controls
- Primary – Wet Wells, Inlets, Collection Chamber
- Secondary – Aeration Basin
- Tertiary – Clarifiers and Disinfection using UV and or Chlorine Dosing
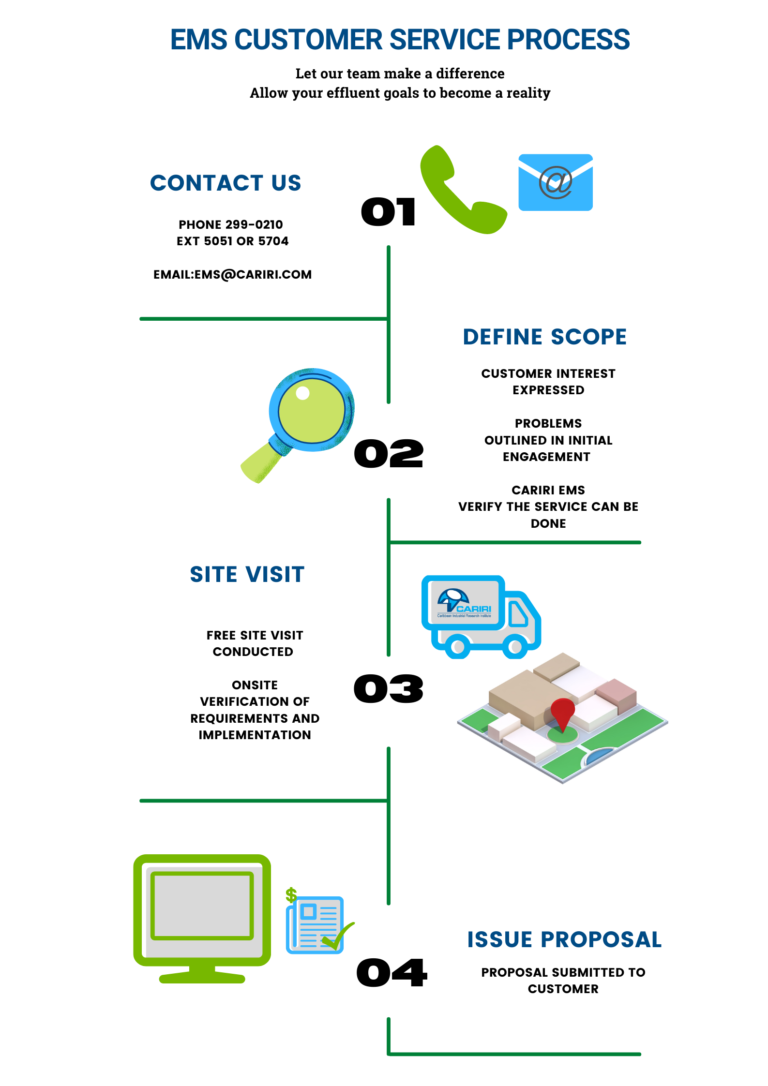
Our Process
Contact Us
- (868) 299 – 0210 ext 5051/5704 or 384 - 7429 (direct contact)
- ssiewah@cariri.com / ems@cariri.com
